Working with Databases ¶
This section will describe how to create a new page that displays country data fetched from
a database table named country. To achieve this goal, you will configure a database connection,
create an Active Record class, define an action,
and create a view.
Through this tutorial, you will learn how to:
- configure a DB connection,
- define an Active Record class,
- query data using the Active Record class,
- display data in a view in a paginated fashion.
Note that in order to finish this section, you should have basic knowledge and experience using databases. In particular, you should know how to create a database, and how to execute SQL statements using a DB client tool.
Preparing the Database ¶
To begin, create a database named yii2basic, from which you will fetch data in your application.
You may create an SQLite, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MSSQL or Oracle database, as Yii has built-in support for many database applications. For simplicity, MySQL will be assumed in the following description.
Info: While MariaDB used to be a drop-in replacement for MySQL this is no longer fully true. In case you wish to use advanced features like
JSONsupport in MariaDB, please check the MariaDB extension listed below.
Next, create a table named country in the database, and insert some sample data. You may run the following SQL statements to do so:
CREATE TABLE `country` (
`code` CHAR(2) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
`name` CHAR(52) NOT NULL,
`population` INT(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0'
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `country` VALUES ('AU','Australia',24016400);
INSERT INTO `country` VALUES ('BR','Brazil',205722000);
INSERT INTO `country` VALUES ('CA','Canada',35985751);
INSERT INTO `country` VALUES ('CN','China',1375210000);
INSERT INTO `country` VALUES ('DE','Germany',81459000);
INSERT INTO `country` VALUES ('FR','France',64513242);
INSERT INTO `country` VALUES ('GB','United Kingdom',65097000);
INSERT INTO `country` VALUES ('IN','India',1285400000);
INSERT INTO `country` VALUES ('RU','Russia',146519759);
INSERT INTO `country` VALUES ('US','United States',322976000);
At this point, you have a database named yii2basic, and within it a country table with three columns, containing ten rows of data.
Configuring a DB Connection ¶
Before proceeding, make sure you have installed both the PDO PHP extension and
the PDO driver for the database you are using (e.g. pdo_mysql for MySQL). This is a basic requirement
if your application uses a relational database.
With those installed, open the file config/db.php and change the parameters to be correct for your database. By default,
the file contains the following:
<?php
return [
'class' => 'yii\db\Connection',
'dsn' => 'mysql:host=localhost;dbname=yii2basic',
'username' => 'root',
'password' => '',
'charset' => 'utf8',
];
The config/db.php file is a typical file-based configuration tool. This particular configuration file specifies the parameters
needed to create and initialize a yii\db\Connection instance through which you can make SQL queries
against the underlying database.
The DB connection configured above can be accessed in the application code via the expression Yii::$app->db.
Info: The
config/db.phpfile will be included by the main application configurationconfig/web.php, which specifies how the application instance should be initialized. For more information, please refer to the Configurations section.
If you need to work with databases support for which isn't bundled with Yii, check the following extensions:
Creating an Active Record ¶
To represent and fetch the data in the country table, create an Active Record-derived
class named Country, and save it in the file models/Country.php.
<?php
namespace app\models;
use yii\db\ActiveRecord;
class Country extends ActiveRecord
{
}
The Country class extends from yii\db\ActiveRecord. You do not need to write any code inside of it! With just the above code,
Yii will guess the associated table name from the class name.
Info: If no direct match can be made from the class name to the table name, you can override the yii\db\ActiveRecord::tableName() method to explicitly specify the associated table name.
Using the Country class, you can easily manipulate data in the country table, as shown in these snippets:
use app\models\Country;
// get all rows from the country table and order them by "name"
$countries = Country::find()->orderBy('name')->all();
// get the row whose primary key is "US"
$country = Country::findOne('US');
// displays "United States"
echo $country->name;
// modifies the country name to be "U.S.A." and save it to database
$country->name = 'U.S.A.';
$country->save();
Info: Active Record is a powerful way to access and manipulate database data in an object-oriented fashion. You may find more detailed information in the Active Record section. Alternatively, you may also interact with a database using a lower-level data accessing method called Database Access Objects.
Creating an Action ¶
To expose the country data to end users, you need to create a new action. Instead of placing the new action in the site
controller, like you did in the previous sections, it makes more sense to create a new controller specifically
for all actions related to the country data. Name this new controller CountryController, and create
an index action in it, as shown in the following.
<?php
namespace app\controllers;
use yii\web\Controller;
use yii\data\Pagination;
use app\models\Country;
class CountryController extends Controller
{
public function actionIndex()
{
$query = Country::find();
$pagination = new Pagination([
'defaultPageSize' => 5,
'totalCount' => $query->count(),
]);
$countries = $query->orderBy('name')
->offset($pagination->offset)
->limit($pagination->limit)
->all();
return $this->render('index', [
'countries' => $countries,
'pagination' => $pagination,
]);
}
}
Save the above code in the file controllers/CountryController.php.
First, The index action calls Country::find(). This find() method creates a ActiveQuery query object, which provides methods to access data from the country table.
To limit the number of countries returned in each request, the query object is paginated with the help of a
yii\data\Pagination object. The Pagination object serves two purposes:
- Sets the
offsetandlimitclauses for the SQL statement represented by the query object so that it only returns a single page of data at a time (at most 5 rows in a page). - It's used in the view to display a pager consisting of a list of page buttons, as will be explained in the next subsection.
Next, all() returns all country records based on the query results.
At the end of the code, the index action renders a view named index, and passes the returned country data as well as the pagination
information to it.
Creating a View ¶
Under the views directory, first create a sub-directory named country. This folder will be used to hold all the
views rendered by the country controller. Within the views/country directory, create a file named index.php
containing the following:
<?php
use yii\helpers\Html;
use yii\widgets\LinkPager;
?>
<h1>Countries</h1>
<ul>
<?php foreach ($countries as $country): ?>
<li>
<?= Html::encode("{$country->code} ({$country->name})") ?>:
<?= $country->population ?>
</li>
<?php endforeach; ?>
</ul>
<?= LinkPager::widget(['pagination' => $pagination]) ?>
The view has two sections relative to displaying the country data. In the first part, the provided country data is traversed and rendered as an unordered HTML list.
In the second part, a yii\widgets\LinkPager widget is rendered using the pagination information passed from the action.
The LinkPager widget displays a list of page buttons. Clicking on any of them will refresh the country data
in the corresponding page.
Trying it Out ¶
To see how all of the above code works, use your browser to access the following URL:
http://hostname/index.php?r=country%2Findex
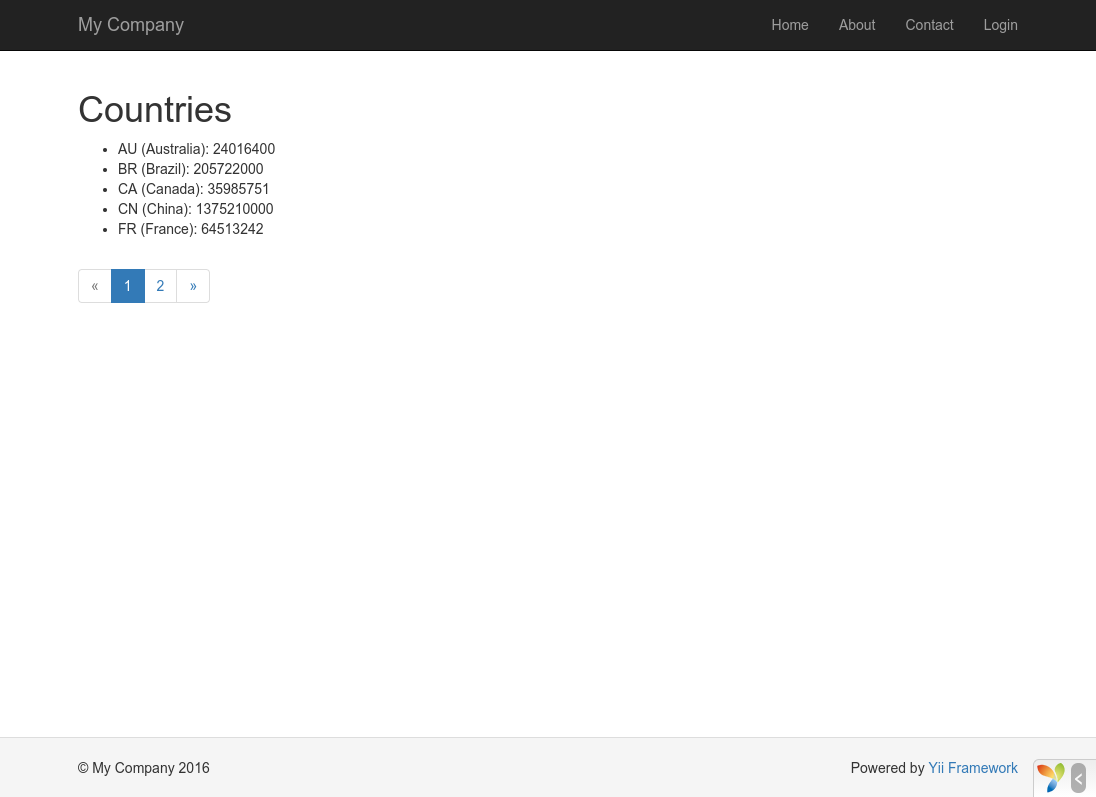
At first, you will see a page showing five countries. Below the countries, you will see a pager with four buttons. If you click on the button "2", you will see the page display another five countries in the database: the second page of records. Observe more carefully and you will find that the URL in the browser also changes to
http://hostname/index.php?r=country%2Findex&page=2
Behind the scenes, Pagination is providing all of the necessary functionality to paginate a data set:
- Initially, Pagination represents the first page, which reflects the country SELECT query
with the clause
LIMIT 5 OFFSET 0. As a result, the first five countries will be fetched and displayed. - The LinkPager widget renders the page buttons using the URLs
created by Pagination. The URLs will contain the query parameter
page, which represents the different page numbers. - If you click the page button "2", a new request for the route
country/indexwill be triggered and handled. Pagination reads thepagequery parameter from the URL and sets the current page number to 2. The new country query will thus have the clauseLIMIT 5 OFFSET 5and return the next five countries for display.
Summary ¶
In this section, you learned how to work with a database. You also learned how to fetch and display data in pages with the help of yii\data\Pagination and yii\widgets\LinkPager.
In the next section, you will learn how to use the powerful code generation tool, called Gii, to help you rapidly implement some commonly required features, such as the Create-Read-Update-Delete (CRUD) operations for working with the data in a database table. As a matter of fact, the code you have just written can all be automatically generated in Yii using the Gii tool.